Contents
- #1: Choosing the Right Binoculars
- #2: Stabilizing Your View
- #3: Dark Adaptation
- #4: Using a Red Flashlight
- #5: Choosing Optimal Locations
- #6: Observing at the Right Time
- #7: Focusing on Specific Objects
- #8: Techniques for Stabilizing Your View
- #9: Panning and Scanning
- #10: Taking Breaks and Relaxing Your Eyes
- #11: Experimenting with Different Magnifications
- Benefits of Using Stargazing Binoculars Correctly
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
- Bottom Line
Gazing up at the night sky has always captivated our imagination. The cosmos, with its twinkling stars, majestic planets, and ethereal nebulae, holds a wealth of wonders waiting to be discovered. While telescopes are commonly associated with astronomy, don’t underestimate the power of binoculars in unlocking the secrets of the universe.
When using binoculars for stargazing and astronomy, choose ones with moderate to high magnification (7x to 10x) and larger objective lens diameter (30mm to 50mm). Stabilize your view with a tripod, allow for dark adaptation, and choose dark-sky locations.
Focus on specific objects, practice panning and scanning, and experiment with different magnifications for optimal results. In this detailed guide, we will delve into a range of tips and techniques to help you maximize the potential of your binoculars for stargazing and astronomy.
#1: Choosing the Right Binoculars
Magnification and objective lens diameter:
Opt for binoculars with a moderate to high magnification (7x to 10x) and a larger objective lens diameter (30mm to 50mm) for better visibility and detail.
Considerations for better light-gathering capability:
Look for binoculars with larger objective lenses as they gather more light, allowing for clearer views of celestial objects, especially in low-light conditions.
Importance of a wide field of view for scanning the night sky:
Select binoculars with a wide field of view to easily scan and navigate the night sky, enabling you to explore a larger area and locate objects more efficiently.
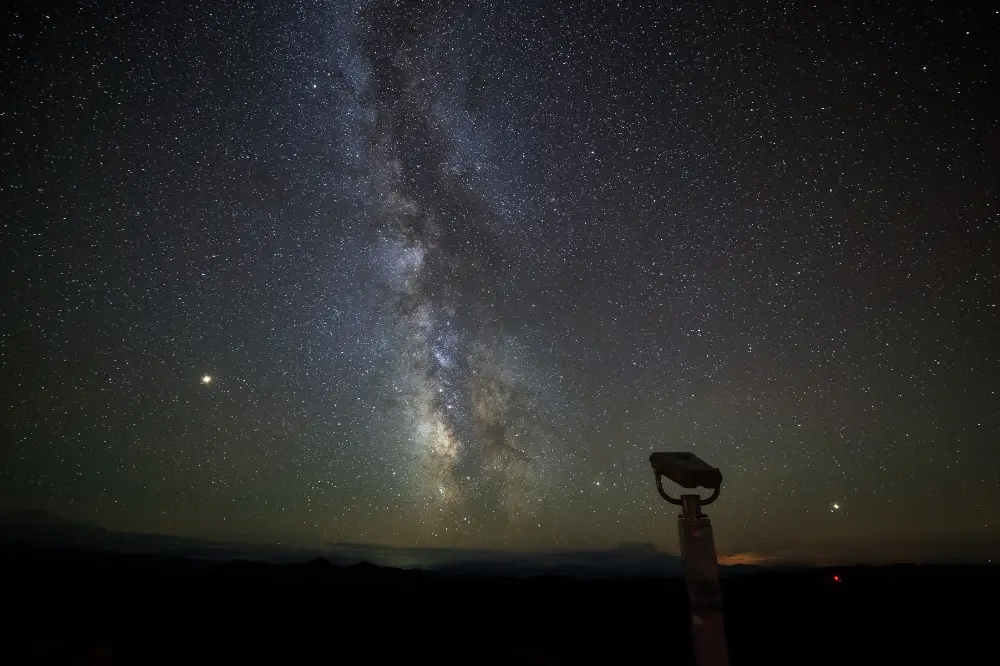

#2: Stabilizing Your View
Benefits of a stable tripod or binocular mount:
Using a tripod or binocular mount provides stability, reducing hand tremors and vibrations, resulting in sharper and clearer images. It also allows for hands-free viewing, enabling longer and more comfortable observation sessions.
Avoiding shaky images and fatigue during longer observation sessions:
Handholding binoculars for extended periods can lead to shaky images and muscle fatigue. By using a stable support like a tripod or binocular mount, you can maintain a steady view for longer durations, minimizing image distortion and reducing strain on your arms and hands.
#3: Dark Adaptation
Dark adaptation process:
Dark adaptation is the adjustment of your eyes to low-light conditions. It takes time for your eyes to become more sensitive to faint light after being exposed to bright surroundings. During this process, the pupils dilate, and the sensitivity of the retinal cells increases, allowing for better perception of dim objects in the night sky.
Tips for minimizing exposure to bright lights before stargazing:
To enhance your dark adaptation, minimize exposure to bright lights before stargazing. Avoid looking at bright screens or using bright lights for at least 30 minutes prior to observing. This allows your eyes to adapt and become more sensitive to the faint light of celestial objects.
Enhancing night vision for better observation:
To maintain optimal night vision, use red lights or filters instead of white lights when necessary. Red light has the least impact on your eyes’ sensitivity to low-light conditions. This way, you can preserve your night vision and enjoy better visibility of the stars, planets, and other celestial wonders.

#4: Using a Red Flashlight
Benefits of preserving night vision with a red flashlight:
Preserving your night vision is crucial for stargazing. Using a red flashlight helps maintain your eyes’ sensitivity to low-light conditions while providing sufficient illumination to read star charts or adjust equipment.
Red light has minimal impact on your night vision, allowing you to continue observing without disrupting your ability to see faint celestial objects.
Appropriate usage for reading star charts and adjusting equipment:
A red flashlight is ideal for tasks that require reading star charts, setting up equipment, or making adjustments in the dark. Its red beam allows you to see details without overwhelming your eyes or causing them to readjust to the darkness.
By using a red flashlight, you can navigate through your observing materials and equipment effectively without compromising your night vision.
#5: Choosing Optimal Locations
Understanding the impact of light pollution on stargazing:
Light pollution from urban areas can significantly diminish the visibility of celestial objects. Understanding the detrimental effects of light pollution helps you appreciate the importance of finding locations with minimal artificial light for a clearer and more immersive stargazing experience.
Identifying dark-sky locations away from city lights:
Seek out dark-sky locations, away from the glare of city lights, to maximize your stargazing opportunities. These areas offer darker skies with less light pollution, allowing you to see a greater number of stars, galaxies, and other celestial phenomena.
Importance of minimizing artificial illumination for better visibility:
When stargazing, minimize the use of artificial lights or cover them with red filters to reduce their impact on your visibility. By minimizing artificial illumination, you create a darker and more natural environment, enhancing your ability to observe and appreciate the faint details of the night sky.
#6: Observing at the Right Time
Planning stargazing sessions on clear, moonless nights:
Clear nights with minimal cloud cover provide optimal conditions for stargazing. Plan your observation sessions when the weather forecast indicates clear skies.
Additionally, try to choose nights when the Moon is not visible or in its crescent phase to minimize its brightness and maximize your ability to see faint objects in the sky.
Managing the impact of moonlight on visibility of faint objects:
Moonlight can significantly affect the visibility of faint celestial objects. Be aware of the Moon’s phase and brightness during your stargazing sessions. If the Moon is bright, focus on observing brighter objects such as planets or star clusters, which can still be seen despite the moonlight.
On darker nights or during the Moon’s crescent phase, you can explore and appreciate fainter objects such as galaxies and nebulae with greater clarity.
#7: Focusing on Specific Objects
Highlighting the importance of observing planets, star clusters, nebulae, and the Moon:
Observing specific celestial objects like planets, star clusters, nebulae, and the Moon provides unique opportunities to witness their distinct features and characteristics.
Planets showcase their intricate atmospheric details, star clusters offer stunning collections of stars, nebulae unveil colorful clouds of interstellar gas, and the Moon reveals its craters and lunar landscapes. Exploring these objects enhances our understanding of the universe and its diverse wonders.
Appreciating the details and beauty of specific celestial objects:
Take the time to appreciate the intricate details and captivating beauty of the objects you observe. Planets exhibit distinct cloud patterns and prominent features like Saturn’s rings or Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. Star clusters unveil a myriad of stars in various shapes and colors.
Nebulae display intricate structures and vibrant hues, while the Moon’s surface showcases its rugged terrain and contrasting landscapes. By focusing on specific objects, you can immerse yourself in the awe-inspiring intricacies of the cosmos and deepen your connection with the wonders of the night sky.

#8: Techniques for Stabilizing Your View
Exploring methods to minimize hand movements and shake:
Minimize hand movements and shake by adopting proper holding techniques for your binoculars. Avoid gripping them tightly and instead use a relaxed grip.
Try to keep your wrists and arms steady, allowing the binoculars to rest against your face for added stability. By consciously reducing hand movements, you can achieve a steadier view and sharper images.
Bracing elbows or using stable surfaces for a steadier view:
To further stabilize your view, utilize techniques such as bracing your elbows against your body or using stable surfaces for support.
Resting your elbows against your chest or leaning against a stable object like a tree or a wall can provide added stability, reducing shake and enhancing the clarity of the observed objects. These techniques help minimize muscle fatigue and enable longer, more comfortable viewing sessions.
#9: Panning and Scanning
Developing a systematic approach to explore the night sky:
Develop a systematic method for panning and scanning the night sky. Start by dividing the sky into sections and focus on one section at a time. Slowly sweep your binoculars across the area, moving in a smooth and controlled manner.
This systematic approach helps you cover more ground and increases your chances of spotting interesting objects or celestial events.
Using naked eye scanning as a starting point before zooming in with binoculars:
Begin your observation by scanning the night sky with your naked eye. Identify prominent stars, constellations, or other celestial landmarks. Once you’ve familiarized yourself with the general layout, use your binoculars to zoom in on specific areas of interest.
This two-step process allows you to get a broader perspective of the sky before narrowing your focus with binoculars, enhancing your overall stargazing experience.
#10: Taking Breaks and Relaxing Your Eyes
Recognizing the intensity of stargazing on the eyes:
Stargazing can be visually intense, as you focus on faint objects against a dark background. The eyes work harder to adapt to low-light conditions and observe details.
Recognizing this intensity helps you understand the importance of taking care of your eyes during extended stargazing sessions.
Importance of taking breaks and avoiding eye strain or fatigue:
To prevent eye strain and fatigue, it’s crucial to take regular breaks during stargazing sessions. Look away from the binoculars or telescope and rest your eyes by focusing on a distant object or closing them for a short period.
Additionally, blink frequently to keep your eyes moisturized. These breaks and relaxation periods help reduce eye strain and maintain visual comfort throughout your stargazing experience.
#11: Experimenting with Different Magnifications
Utilizing variable magnification settings for different objects:
Take advantage of the variable magnification settings of your binoculars to optimize your observations of different celestial objects. Higher magnifications can bring distant objects closer and reveal finer details, making them ideal for observing planets or compact star clusters.
Lower magnifications provide a wider field of view, which is beneficial for scanning large areas of the sky or observing extended objects like nebulae or galaxies.
Balancing between closer views and wider field of view:
Finding the right balance between closer views and a wider field of view is key to a fulfilling stargazing experience. While higher magnifications offer more detailed views, they also narrow the field of view, making it harder to locate objects.
On the other hand, lower magnifications provide a broader perspective of the night sky, allowing you to appreciate the vastness and context of celestial objects. Experiment with different magnifications to strike the right balance between getting closer to specific objects and enjoying the broader celestial tapestry.
Benefits of Using Stargazing Binoculars Correctly
Using binoculars for stargazing and astronomy offers several benefits that enhance the overall observing experience. Here are some key advantages:
Portability and Versatility: Binoculars are compact and lightweight, making them highly portable. They can be easily carried to different observing locations, allowing you to explore the night sky wherever you go. Their versatility makes them suitable for various celestial observations, including scanning the sky, observing star clusters, planets, and even the Moon.
Enhanced Detail and Immersion: Binoculars provide a closer and more detailed view of celestial objects compared to the naked eye. They reveal intricate features on the Moon’s surface, bring out the intricate patterns of star clusters, and highlight the subtle details of planets. This enhanced level of detail allows for a more immersive experience, enabling you to appreciate the beauty and complexity of the cosmos.
Wide Field of View: Binoculars offer a wider field of view compared to telescopes, allowing you to observe larger sections of the sky. This broader perspective is particularly useful for locating objects, scanning constellations, and exploring wide areas of interest. It helps you navigate the night sky more efficiently and offers a better sense of the overall celestial landscape.
Ease of Use: Binoculars are generally easy to use, even for beginners. They require minimal setup and have a straightforward operation, making them accessible to stargazers of all levels of expertise. With basic adjustments, such as focusing and adjusting the interpupillary distance, you can quickly start observing celestial objects without the need for complex alignment procedures or extensive technical knowledge.
Cost-Effective: Binoculars are typically more affordable than telescopes, making them an excellent entry point into stargazing and astronomy. They offer a cost-effective option for those who want to explore the night sky without investing in high-end equipment. Binoculars can deliver impressive views of celestial objects within a reasonable budget, making astronomy accessible to a broader range of enthusiasts.
Sharpening Observation Skills: Using binoculars for stargazing and astronomy helps develop observation skills. By honing your ability to locate and identify celestial objects, you become more adept at navigating the night sky. Binoculars encourage a more active and engaged observing process, enabling you to spot subtle details and patterns that may go unnoticed with the naked eye alone. This practice improves your overall astronomical knowledge and appreciation of the cosmos.
Shared Observing Experience: Binoculars can be shared among multiple observers, allowing for a shared stargazing experience. Whether with family, friends, or fellow astronomy enthusiasts, using binoculars encourages collaboration and engagement. Observing together fosters a sense of community, facilitates knowledge-sharing, and enhances the enjoyment of exploring the night sky.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) and answers about using an air fryer for the first time:
Q: What are the recommended magnification and objective lens size for binoculars used in stargazing and astronomy?
A: It is generally recommended to opt for binoculars with a magnification between 7x and 10x for stargazing. As for the objective lens size, a diameter ranging from 30mm to 50mm is suitable, as it allows for better light gathering and improved visibility in low-light conditions.
Q: How can I stabilize my binoculars to minimize shake and improve image clarity?
A: To stabilize your binoculars, you can use a tripod adapter or a dedicated binocular mount. Alternatively, you can brace your elbows against a solid surface or use a bean bag for support. These methods help reduce hand movements and ensure a steadier view.
Q: How long does it take for dark adaptation to occur, and why is it important for stargazing?
A: Dark adaptation is the process by which your eyes adjust to low-light conditions. It takes approximately 20-30 minutes for your eyes to adapt fully. It is important for stargazing because dark adaptation enhances your ability to see faint celestial objects and increases overall visibility in the night sky.
Q: Why is using a red flashlight recommended for stargazing?
A: Red flashlights are recommended because they have the least impact on your night vision. The red light allows you to read star charts and adjust your equipment without disrupting your eyes’ adaptation to the darkness. It helps preserve your night vision and allows you to see faint celestial objects more clearly.
Q: How can I find dark-sky locations for optimal stargazing?
A: Dark-sky locations are areas away from city lights that provide minimal light pollution, allowing for better visibility of celestial objects. National parks, rural areas, and designated observatories often offer ideal dark-sky conditions. Online resources, such as light pollution maps and astronomy apps, can help you identify suitable locations near you.
Q: Are there specific objects that are recommended for observation with binoculars?
A: Yes, binoculars are great for observing a range of celestial objects. Planets like Jupiter and Saturn reveal their moons and surface details. Star clusters, such as the Pleiades or the Beehive Cluster, showcase groups of stars. Nebulae like the Orion Nebula display intricate structures of glowing gas. The Moon also offers fascinating details like craters and mountain ranges, perfect for binocular observation.
Q: Can I use binoculars during the day for terrestrial observation as well?
A: Absolutely! Binoculars are versatile and can be used for both astronomical and terrestrial observations. Whether you want to enjoy nature walks, birdwatching, or sporting events, binoculars provide a closer and more detailed view of distant objects during daylight hours.
Bottom Line
Equipped with these invaluable tips, you’re now prepared to embark on a captivating stargazing journey with your binoculars as your trusty guide.
Remember to choose the right binoculars, stabilize your view, preserve night vision, select optimal locations, and focus on specific objects. Take your time, savor each moment, and let the universe unfold before your eyes. Happy stargazing!
A Binoculars enthusiast, who love exploring skies and watching birds. It is my hobby to collect Binoculars of different kinds and try to explore the world through various lenses. This is all I do to explore happiness by magnifying my beautiful world.




