Contents
From the towering peaks of distant mountains to the delicate feathers of a bird in flight, the world around us is an exquisite tapestry of wonders waiting to be discovered. Binoculars, the versatile optical devices, allow us to peer into this enchanting realm with enhanced clarity and precision.
Binoculars are a useful tool for observing the environment and bringing subjects at a great distance closer. There are different types of binoculars for every use situation, and choosing the right one starts with knowing what’s actually available.
In this article, we will explore the different binocular magnification ranges and their ideal uses.
Magnification — Explained
Binoculars are often referred to as two numbers separated by an “x”. For example, 8×32. The first number is the power or magnification of the binocular. With an 8×32 binocular, the object being viewed appears to be eight times closer than you would see it with the unaided eye.
Most binoculars offer somewhere between 8 and 12 times magnification, as this is generally the ideal range for bird watching and general use. However, some people can use binoculars with a magnification even of 15x, but you need to have a very steady hand.
Understanding Binocular Magnification
Before we venture into the world of varying magnification ranges, it’s essential to understand the concept of binocular magnification.
Represented by a number followed by an “x” (e.g., 8x or 10x), binocular magnification indicates how much larger an object appears through the binoculars compared to its size when observed with the naked eye.
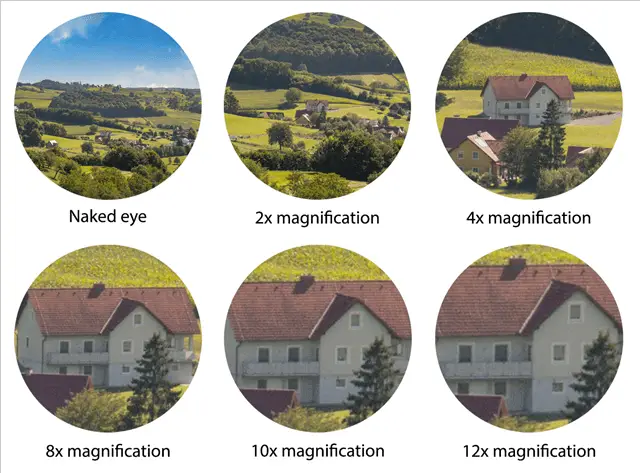

Higher magnification provides a more detailed view, but may come with trade-offs like a narrower field of view and reduced brightness.
Types of Binocular Magnification Ranges
Low Magnification (2x to 7x):
- Characteristics: Binoculars with a magnification range of 2x to 7x are considered low magnification. They provide a wider field of view, making it easier to scan and track moving objects.
- Ideal uses and activities: These binoculars are perfect for activities like birdwatching, nature observation, and sports events. Their broader view allows you to follow fast-moving birds or sports action without losing sight of the bigger picture.
- Pros: Brighter images, ease of use without the need for stabilization, suitable for low-light conditions.
- Cons: Limited detail for distant subjects.
Medium Magnification (8x to 12x):
- Characteristics: Medium magnification binoculars, ranging from 8x to 12x, strike a balance between detail and field of view. They offer more magnification than low range but maintain a respectable viewing width.
- Ideal uses and activities: These binoculars excel in birdwatching and wildlife observation, as they provide better detail for observing animals or celestial objects.
- Pros: Improved detail compared to low magnification, versatility for various outdoor activities.
- Cons: Slightly narrower field of view, may require some stabilization.

High Magnification (12x and above):
- Characteristics: High magnification binoculars, starting from 12x and above, are designed for detailed, long-range observation.
- Ideal uses and activities: Astronomers and those seeking intricate details of distant subjects, like wildlife in vast landscapes, benefit greatly from high magnification binoculars.
- Pros: Exceptional detail and clarity, suitable for astronomy and long-distance terrestrial viewing.
- Cons: Narrow field of view, challenging to keep steady without stabilization.
Choosing the Right Magnification for Specific Activities
Birdwatching and Wildlife Observation:
- Recommended magnification range: 8x to 10x
- Why this range is ideal: Strikes a balance between detail and a wider field of view, perfect for observing birds and animals in their natural habitats.
- Examples of suitable binocular models: Nikon Monarch 8×42, Vortex Diamondback HD 10×42.
Astronomy and Stargazing:
- Recommended magnification range: 10x to 15x or higher
- Why this range is ideal: Provides detailed views of celestial objects like the moon, planets, and star clusters.
- Examples of suitable binocular models: Celestron SkyMaster 15×70, Orion Scenix 10×50 Wide-Angle.
Sports and Events:
- Recommended magnification range: 7x to 10x
- Why this range is ideal: Allows you to capture fast-paced action with a wider field of view, making it easier to follow athletes during sports events.
- Examples of suitable binocular models: Bushnell H2O 10×42, Canon 10×30 IS II.
Hiking and Outdoor Adventures:
- Recommended magnification range: 8x to 10x
- Why this range is ideal: Offers a versatile magnification range for observing wildlife and breathtaking landscapes during outdoor expeditions.
- Examples of suitable binocular models: Leica Trinovid 8×32, Swarovski CL Companion 10×30.
Finding the Perfect Balance
While magnification plays a crucial role in your binocular selection, it’s essential to consider other factors like field of view, exit pupil, and objective lens size.
A wider field of view is advantageous for tracking moving subjects, while a larger exit pupil enhances low-light performance. Additionally, larger objective lenses gather more light, resulting in brighter images.
Ideal Uses
The use you intend to put your binoculars to will help you decide which magnification is best, but generally, you will find that lower magnifications offer a brighter image and are easier to hold steady in the hands.
- For general usage, 8x or 10x magnification is the right one for you due to the possibility to use those binoculars handheld without the need for a tripod.
- A 8x magnification binocular has always been the most popular option, especially for bird and wildlife observation.
- 10x is the next magnification up and is a common alternative, and some models also come in a 12x magnification.
- For birdwatching, tracking moving objects, and keeping shaking to a minimum, 8 to 10x magnification is best.
- For theater going, a somewhat lower magnification is easier to use, and portability is an important factor.
- For long-range shooting, such as varmint hunting, more powerful binoculars like 12×40 to 16×50 are best.
Other Factors to Consider
- The second number in the formula (8×32) is the diameter of the objective or front lens in millimeters.
- The larger the objective lens, the more light that enters the binocular, and the brighter the image.
- Binoculars range in size from pocket-friendly compact models to giant contraptions meant for stargazing or dramatically panning the horizon from the bridge of a large ocean liner.
- Additionally, there are different types of binoculars, including roof prism, porro prism, and monocular, optimized for different uses.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
What is binocular magnification, and how does it affect my viewing experience?
Binocular magnification refers to how much larger an object appears through the binoculars compared to its actual size. Higher magnification provides more detailed views, but may result in a narrower field of view and reduced brightness. Lower magnification offers a wider view, making it easier to track moving subjects.
Which magnification range is best for birdwatching and wildlife observation?
For birdwatching and wildlife observation, a magnification range of 8x to 10x is ideal. This range strikes a balance between detail and a wider field of view, allowing you to observe birds and animals in their natural habitats with ease.
Are high magnification binoculars suitable for stargazing and astronomy?
Yes, high magnification binoculars (10x to 15x or higher) are excellent for stargazing and astronomy. They provide detailed views of celestial objects like the moon, planets, and star clusters, enhancing your astronomical experience.
Can low magnification binoculars be used for sports events?
Absolutely! Low magnification binoculars (2x to 7x) are well-suited for sports events, providing a wider field of view, making it easier to follow fast-paced action and capture the excitement of sports events.
What are the pros and cons of medium magnification binoculars?
Medium magnification binoculars (8x to 12x) offer improved detail compared to low magnification and are versatile for various outdoor activities. However, they may have a slightly narrower field of view and may require some stabilization for extended use.
What are some recommended binocular models for stargazing and astronomy?
Examples of suitable binocular models for stargazing and astronomy include the Celestron SkyMaster 15×70 and the Orion Scenix 10×50 Wide-Angle.
Are higher magnification binoculars harder to keep steady?
Yes, higher magnification binoculars (12x and above) can be more challenging to keep steady without stabilization. Tripods or image stabilization features can help mitigate image shake for prolonged use.
Can binoculars with low magnification be used for birdwatching in low-light conditions?
Yes, binoculars with low magnification are suitable for birdwatching in low-light conditions. Their wider field of view allows more light to enter the binoculars, resulting in brighter images.
What should I consider when choosing the right magnification for my needs?
Consider your intended use, stability requirements, and other factors like field of view, exit pupil, and objective lens size. For specific activities like birdwatching, stargazing, sports events, or hiking, match the magnification range to your preferences and needs.
Are there any trade-offs when choosing higher magnification binoculars?
Yes, higher magnification binoculars may have a reduced field of view and can be more challenging to keep steady. These trade-offs should be considered, especially if you plan to use binoculars for extended periods. Image stabilization features or using a tripod can help overcome some of these challenges.
Conclusion
For general usage, 8x or 10x magnification is the right one for you due to the possibility to use those binoculars handheld without the need for a tripod.
However, for specific activities such as birdwatching, tracking moving objects, and long-range shooting, higher magnifications may be required. Remember to also consider the size of the objective lens and the type of binoculars when making your selection.
A Binoculars enthusiast, who love exploring skies and watching birds. It is my hobby to collect Binoculars of different kinds and try to explore the world through various lenses. This is all I do to explore happiness by magnifying my beautiful world.




